Ceramic Capacitor Dielectric Classes
Ceramic dielectric types
Ceramic capacitor can utilize a whole host of different dielectrics unlike other capacitor types including tantalum capacitors and electrolytic capacitors. These different dielectrics give the capacitors very different properties, so apart from choosing that a ceramic capacitor is to be used, a second decision about the specific type of dielectric may also be needed.
Mention is often made of common ceramic capacitor dielectrics including C0G, NP0, X7R, Y5V, Z5U and many more will be seen specified in distributors list. But knowing which type is best requires a little further investigation.
Ceramic capacitor dielectric classes
In order to simplify the selection of capacitors with the required dielectric, some industry organizations have defined a number of ceramic dielectric application classes.
These application classes split the different dielectrics available for ceramic capacitors into different classes according to the anticipated application.
CERAMIC CAPACITOR DIELECTRIC APPLICATION CLASSES
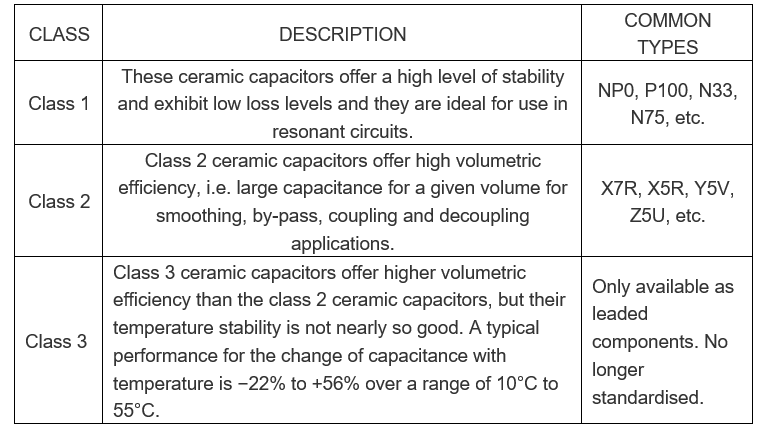
These ceramic capacitor classes are standardised by international bodies including the IEC, International Electrotechnical Commission and the EIA, Electronic Industries Alliance.
Class 1 ceramic capacitor dielectric
Ceramic capacitors that use class 1 dielectrics offer the highest performance in terms of stability and loss. They can provide accurate high tolerance capacitors with stable voltage and temperature coefficients. They also offer low losses and are therefore suitable for use in oscillators, filters and the like.
Class 1 ceramic dielectrics are normally based on finely ground materials like Titanium dioxide (TiO2), with additives of Zinc, Zirconium, Niobium, Magnesium, Tantalum, Cobalt and Strontium, although many modern C0G (NP0) formulations contain neodymium, samarium and other rare earth oxides.
Class 1 capacitor codes:
To define the performance of a ceramic capacitor dielectric a three character code is used which is specific to ceramic capacitor class 1 dielectrics.
The first character is a letter which gives the significant figure of the change in capacitance over temperature in ppm/°C
The second character is numeric and gives the multiplier
The third character is a letter and gives the maximum error in ppm/C
The table below details what each of the EIA codes means.
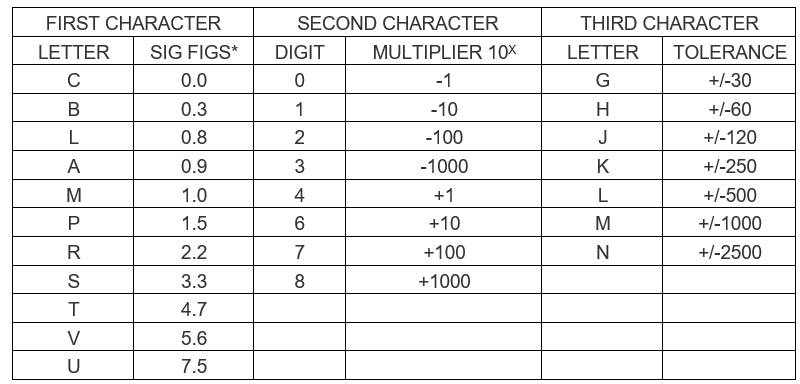
As an example, one common type of class 1 capacitor is a C0G and this will have 0 drift, with an error of ±30ppm/°C.
C0G (NP0) is the most popular formulation of the EIA Class 1 ceramic materials.
C0G (NP0) ceramics offer one of the most stable capacitor dielectrics available. Capacitance change with temperature is 0 ±30ppm/°C which is less than ±0.3% ΔC from -55°C to +125°C. Capacitance drift or hysteresis for C0G (NP0) ceramics is negligible at less than ±0.05% versus up to ±2% for films.
The C0G (NP0) ceramic dielectric usually has a “Q” in excess of 1000 and shows little capacitance or “Q” changes with frequency. In addition to this, the dielectric absorption is typically less than 0.6% which is similar to mica which is renowned for having a very low absorption.
Class 2 ceramic capacitor dielectric
Ceramic capacitor class 2 dielectrics have a much higher level of permittivity than their class 1 counterparts. This gives them a much higher capacitance level for a given volume, i.e. better volumetric capacitance efficiency. However this is at the expense of accuracy and stability. In addition to this they exhibit a non-linear temperature coefficient and a capacitance that is dependent to a small degree on the applied voltage.
As a result of these characteristics, they are ideal for decoupling and coupling applications where the exact value of capacitance is not critical, but where space may be an issue.
Class 2 capacitor codes
A three code is used to define the performance of ceramic capacitor dielectric.
The first character is a letter. This gives the low-end operating temperature.
The second is numeric and indicates the high-end operating temperature.
The third character is a letter which indicates the capacitance change over the temperature range.
The table below details what each of the EIA codes means.
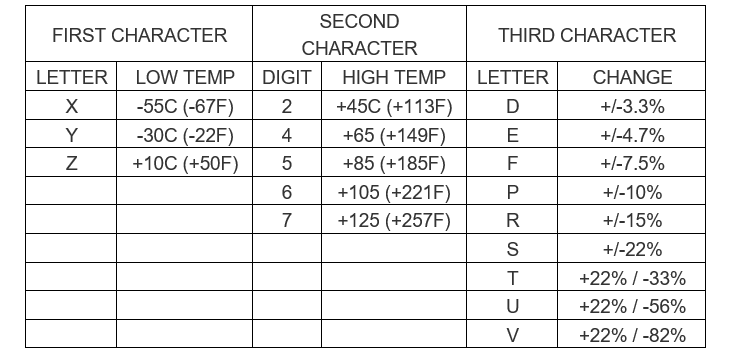
Popular class 2 ceramic dielectrics include X7R which as a temperature range of −55 to+125°C, with a ΔC/C0 of ±15%, Y5V which as a temperature range of −30 to+85°C with a ΔC/C0 of +22/−82%, and Z5U which has a temperature range of +10 to +85°C and a ΔC/C0 = +22/−56%.
There is a wide variety of dielectrics that can be used for ceramic capacitors. Their performance is carefully tailored to ensure they meet the required performance levels. When choosing a ceramic capacitor for a particular application, referring to the tables above can provide the required insight.
Ceramic capacitor summary
Ceramic capacitors are widely used in modern electronics manufacture. Although ceramic capacitors initially appeared as leaded electronic components, as surface mount technology took off for mass production, they soon appeared as surface mount capacitors. Today the multilayer ceramic capacitors are produced in vast quantities and complement the performance of other capacitors like electrolytic capacitors and tantalum capacitors that tend to be used for the higher values above 1µF.

